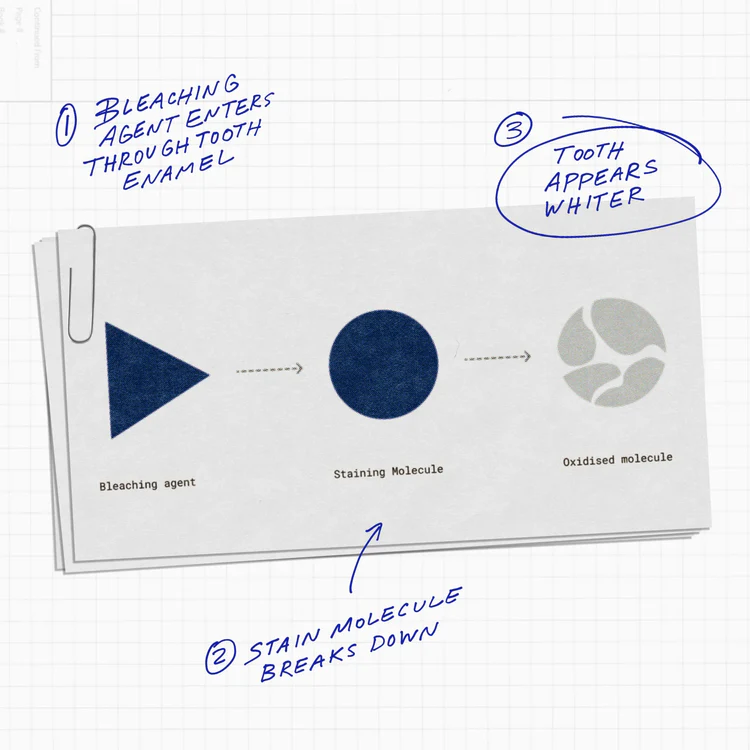
ما هو تبييض الأسنان؟
تغيّر لون الأسنان وظهور البقع ينتج عن التصاق أصباغ وملوّنات مختلفة بالمواد العضوية الموجودة على سطح السن. وتُزال هذه البقع بطريقتين رئيسيتين: الإزالة الفيزيائية والتبييض الكيميائي.
تستهدف الإزالة الفيزيائية البقع السطحية من خلال كشط أو صقل الطبقة الخارجية للسن. أما التبييض الكيميائي فيزيل البقع السطحية والعميقة، وهو الأكثر شيوعًا وفعالية.